The Basics of Podokesaurus, Dinosaurs and Fossils
by Pat Monteith
What is a dinosaur?

Long before there were people, there were dinosaurs.Dinosaurs are actually reptiles that lived on land. They came in different shapes and sizes but unlike reptile crocodiles and lizards, dinosaurs had their legs positioned directly under their bodies with legs perpendicular to their bodies. This allowed them to run faster, use less energy and do a better job of supporting their weight. They also had two holes behind their eye sockets and large strong jaw muscles. Like other reptiles they laid, and were hatched from eggs.
There were many different kinds of dinosaurs.

Marcin Chady – Wikimedia Link
Triceratops vs Tyrannosaurus rex
CC BY 2.0 File:Triceratops-vs-T-Rex001.jpg, Created: 14 August 2009
There are more than 1,000 species of dinosaurs, but dinosaurs could not fly and none of them lived in the water. Some walked on two legs and some walked on four legs. Some of them could do both. Some were really fast and some were slow. Some dinosaurs had horns and spikes and bumpy skin. Some even had feathers.
When did dinosaurs live?
Dinosaurs lived for more than 140 million years starting at the beginning of the Triassic Period. Most dinosaurs became extinct about 66 million years ago…except for birds. When the dinosaurs lived, Earth’s continents were smooshed together into one big continent called Pangea and Earth was much warmer than it is now.
Is a bird a dinosaur?
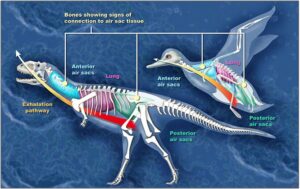 Yes, all birds like the ones in your backyard are also relatives of and ancestors of dinosaurs. They both have three toes, an s-shaped neck, hollow bones efficient lungs, similar claws and have scales on their feet. Birds actually evolved from a group of meat-eating dinosaurs called theropods. Tyrannosaurus rex belonged to the theropod group but birds evolved from small theropods. The oldest bird fossils are about 150 million years old, but bird fossils are unusual because bird bones are hollow and fragile.
Yes, all birds like the ones in your backyard are also relatives of and ancestors of dinosaurs. They both have three toes, an s-shaped neck, hollow bones efficient lungs, similar claws and have scales on their feet. Birds actually evolved from a group of meat-eating dinosaurs called theropods. Tyrannosaurus rex belonged to the theropod group but birds evolved from small theropods. The oldest bird fossils are about 150 million years old, but bird fossils are unusual because bird bones are hollow and fragile.
Why aren’t there any other dinosaurs around besides birds?
 As you can see in the Dinosaur Timeline above, dinosaurs became “extinct” or died out a very long time ago, about 65 million years ago. Many scientists believe dinosaurs became extinct because of a big asteroid that hit Earth near Mexico causing climate changes that destroyed their food supply. There is a crater, or big hole in the ground, off the coast of Mexico that is 93 miles in diameter and goes 12 miles deep.
As you can see in the Dinosaur Timeline above, dinosaurs became “extinct” or died out a very long time ago, about 65 million years ago. Many scientists believe dinosaurs became extinct because of a big asteroid that hit Earth near Mexico causing climate changes that destroyed their food supply. There is a crater, or big hole in the ground, off the coast of Mexico that is 93 miles in diameter and goes 12 miles deep.
Is a dinosaur the same as a fossil?

Source James St. John, CC BY 2.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
No. Fossils are the bones, remains and other preserved parts of ancient plants and animals. The only way we have to learn about dinosaurs is by studying fossils. Most fossils are found in deserts or are dug up from special types of rocks, called sedimentary rocks. But fossils don’t really have any bone material in them. A fossil has the same shape as its original thing but is chemically more like a rock. You can find most fossils or copies of their bones and teeth in natural history museums. Massachusetts has a state fossil — dinosaur tracks, and soon we will also have a state dinosaur — the Podokesaurus; the plan is for Massachusetts to have both of these official state “things” and not to replace our current “state fossil” with our new “state dinosaur.”
How are we able to know what dinosaurs looked like if they’ve been dead for so long?

Eduard Solà, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons – Source
Some animals were buried very quickly after they died by being covered by mud or by a sand storm. The parts of the animals that didn’t rot such as hard bones and teeth were surrounded by the sedimentary rock material. Over time, water with minerals soaked into the bone and the spaces in the bones, and replaced the chemistry of the bone with minerals like calcite, silica, pyrite and iron, which turned them into rocks. But most dinosaurs did not fossilize and we only know about the fossils remains we can find.
How are fossils dug out of the ground?

Virginia State Parks staff, CC BY 2.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0>, via Wikimedia Commons – Source
After it’s found, a fossil must be very carefully taken out of the dirt and rock around it so the fossil does not break, crumble or otherwise get destroyed because it might have been in the ground for thousands or millions of years. Large fossils are dug up differently from small fossils, with tools like shovels and sometimes jack-hammers are used. With smaller fossils, a researcher might use a dental pick and paint brush. In either case, it is extremely important to make sure all related information is recorded about the position of the fossils, geographical coordinates, and photos. In some cases, the dirt (called matrix) surrounding the fossil is also included, then it is all wrapped up in paper or cloth with a layer of plaster surrounding it all. When this is done, the fossil is not actually removed until it’s back in the lab.
Where are dinosaur fossils found?

Greg Willis from Denver, CO, usa, CC BY-SA 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons – Source
Scientists who study geology and biology are called paleontologists; they have been finding dinosaur fossils for hundreds of years all over the world. The first fossil bones were found in the late 1700s in New Jersey and in England. But in 1800, a farmer found 1-foot-long fossilized footprints at his farm in Granby, MA near Hadley and Amherst. It was determined they came from a theropod dinosaur 50 feet in length that made the tracks more then 200 million years ago.
Where can we see the Podokesaurus fossil?
Unfortunately, the original fossil of the Podokesaurus was destroyed in a museum fire in 1917 and no remains of the fossil were found in the ruins. Before it was destroyed, a cast of the fossil was made at the Peabody Museum of Natural History at Yale University. There is also a cast at the Amherst College Beneski Museum. Here’s what the cast of it looks like:

Did the Podokesaurus live where its bones were found?
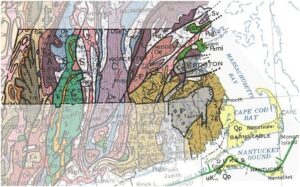
Maybe, but probably not. The geology (study of rocks) of Massachusetts as shown here in the rock formation of Massachusetts indicates that there were lots of ice glaciers and earthquake seismic activity that moved the ground around. Near the Western part of MA where the Connecticut River Valley formed, there were many glaciers that would pick up boulders and move them far away from their original resting place, and then drop them. Podokesaurus was thought to have been found in a glacial boulder that was moved far from its original position. So, we really don’t know quite where Podokesaurus is from.